The world of power distribution is undergoing a significant transformation. GIS substation technology is at the forefront of this revolution. This advanced approach offers enhanced efficiency and reliability in electricity management. Unlike traditional substations, GIS substation systems require less space and are more adaptable. This miniaturization is a game-changer in urban areas where land is scarce.
With the rise of renewable energy sources, the need for efficient power distribution is critical. GIS substation technology simplifies the integration of these sources into the grid. It allows for real-time monitoring and control, providing a more responsive grid. However, the implementation of GIS substation can come with challenges. The initial investment is substantial, and skilled labor is necessary for maintenance.
Despite these issues, the benefits are compelling. GIS substations promise improved safety and reduced maintenance costs over time. As cities grow, this technology may well be the key to a sustainable power future. Reflecting on its potential reveals a landscape ripe for innovation, yet it is essential to address the hurdles involved. Balancing progress with practicality is crucial in realizing the full benefits of GIS substation technology.

GIS substation technology is transforming power distribution by enhancing efficiency and reliability. This technology integrates geographical information systems with substation management. It enables operators to visualize and manage electrical grids effectively. With real-time data, decision-making becomes faster and more accurate. Operators can identify issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime.
The impact on efficiency is significant. GIS technology maps out infrastructure, allowing for better route optimization of power flow. It reduces energy loss, which is vital in today's energy-consuming world. However, this technology is not without challenges. Data management requires skilled personnel and constant updates. If not handled well, data inconsistency may lead to misguided decisions. Additionally, the initial costs for implementing GIS systems can be high, deterring some organizations from adopting this tech.
Overall, GIS substation technology offers immense potential to revolutionize power distribution. While it improves operational efficiency, organizations must remain vigilant about the challenges it presents. Embracing this technology requires a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation. Power distribution can be more efficient, but success hinges on the quality of data management and workforce training.
Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) substations are transforming how power distribution is managed today. One key feature of GIS technology is its compact design. These substations occupy less space compared to traditional air-insulated switchgear. In urban areas, this is crucial. Industry reports indicate that GIS can reduce land requirements by up to 80%. This compactness allows for better land use in densely populated cities.
Another significant advantage lies in reliability and safety. GIS systems are less exposed to weather elements. This minimizes the risk of failures during storms or extreme conditions. According to recent data, GIS substations have a failure rate of less than 1%. Furthermore, their enclosed design reduces the risk of electrical hazards, enhancing worker safety. However, the high initial investment remains a concern. Organizations must weigh long-term benefits against upfront costs.
Maintenance is also essential. While GIS technology generally requires less maintenance, skilled personnel are necessary for servicing. Reports highlight a shortage of trained technicians in some regions. Addressing this skill gap is vital for maximizing GIS's potential in power distribution. Thus, though GIS substations offer many benefits, challenges remain that need thoughtful solutions.
| Feature | Description | Benefit | Impact on Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Design | GIS substations occupy less space compared to traditional substations. | Reduces land use and installation costs. | Less exposure to surrounding areas, minimizing risks. |
| Sealed Components | Sealed tanks prevent environmental contamination. | Improves environmental compliance. | Reduces the risk of accidents due to leaks. |
| Enhanced Reliability | Less maintenance needed due to durable materials. | Increases uptime and efficiency of power distribution. | Minimizes risk of power outages and hazards. |
| Remote Monitoring | Allows for real-time data tracking and analysis. | Facilitates quicker response times to faults. | Improves safety measures through timely interventions. |
| Integrated Protection Systems | Smart technology predicts and prevents failures. | Enhances overall system reliability. | Reduces risk of catastrophic failures. |
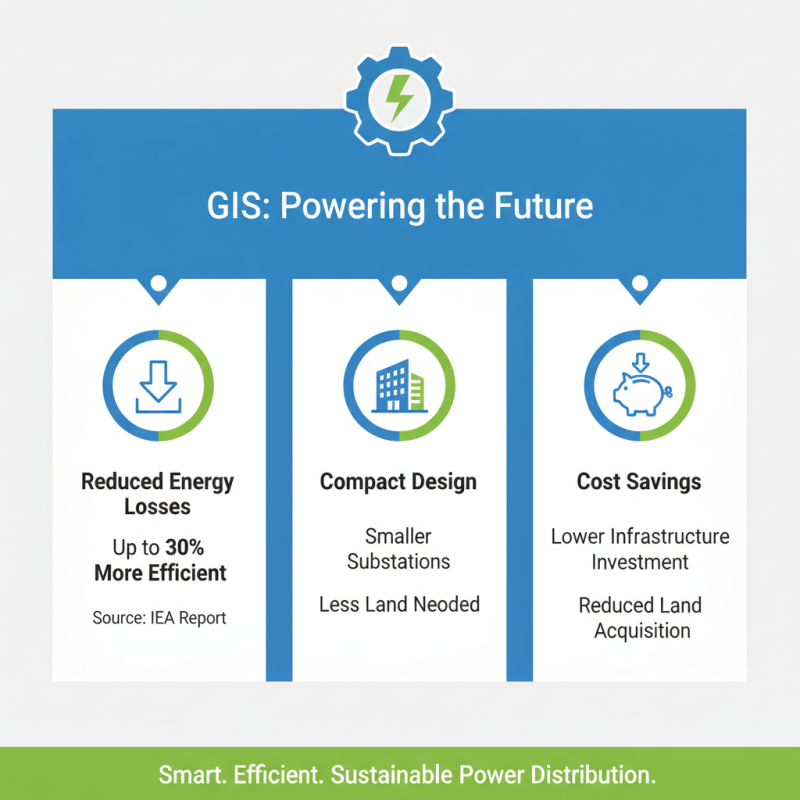
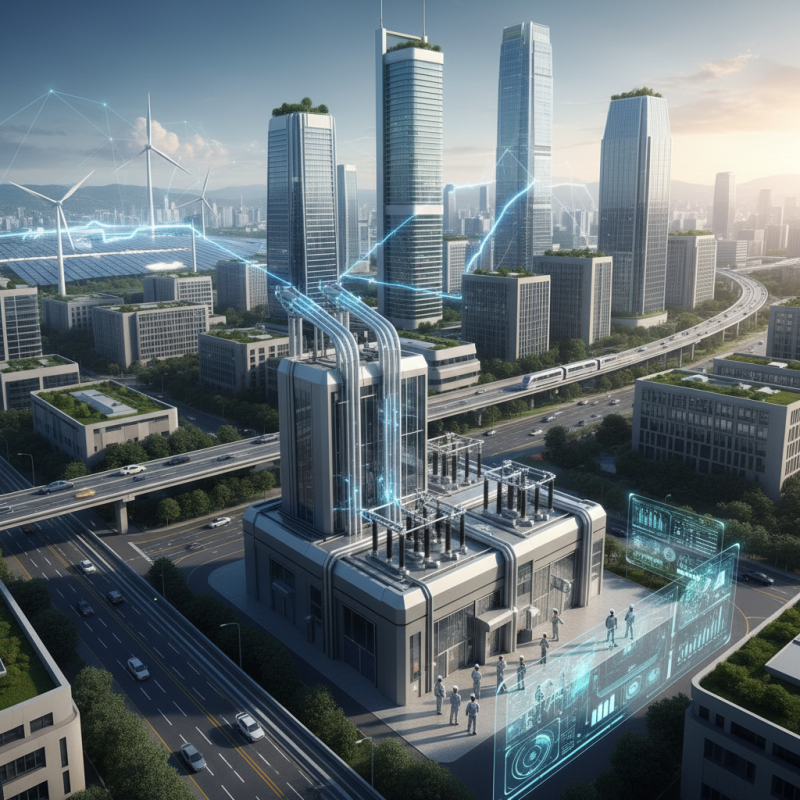
GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear) technology is making significant strides in power distribution. A report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that GIS systems can reduce energy losses by up to 30%. This efficiency is due to their compact design, which allows for smaller substations. The result? Lower land acquisition costs and less infrastructure investment.
Moreover, GIS technology requires minimal maintenance. Traditional air-insulated substations often need regular upkeep, which can be costly. According to a study by Frost & Sullivan, maintenance costs for GIS are up to 50% lower than those for conventional systems. This reduction in ongoing expenses translates into better financial performance for utility companies.
Yet, implementation isn't without challenges. The initial investment for GIS is higher than traditional methods. Some utilities hesitate, concerned about capital expenditures. This hesitance can be a missed opportunity. As demand for reliable power grows, embracing GIS can lead to long-term savings. The shift is daunting, but the data suggests it’s a necessary evolution for modern power grids.
Switching to GIS-based substation systems is a significant step toward environmental sustainability. These systems require less physical space than traditional substations, reducing land use. Compact designs minimize the ecological footprint. Additionally, GIS substations are often more efficient in energy management. They contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions. This shift is crucial in the fight against climate change.
Moreover, GIS technology enhances operational reliability. Fewer components generally mean less maintenance. This leads to less waste over time. While traditional substations may lead to environmental contamination from leaks and spills, GIS systems are sealed more effectively. However, implementing this technology involves challenges. The initial investment can be high, and training is necessary.
Despite these hurdles, the long-term benefits outweigh the drawbacks. Reduced land disruption and lower emissions paint a promising picture. Communities could experience improved air quality and reduced noise pollution. While there is still room for improvement, the potential is enormous. GIS substation technology is a vital part of a greener power distribution future.
This chart illustrates the energy efficiency of traditional substations compared to GIS-based substations, highlighting the significant improvements in efficiency when switching to GIS technology.
The rapid advancement of GIS substation technology is reshaping how we approach power distribution. Notably, the International Energy Agency reported that GIS substations can reduce space utilization by up to 80%. This efficiency is essential in urban settings where land availability is limited. However, there can be challenges with the initial investment costs that may deter smaller utilities from adopting this technology.
Future trends indicate a strong movement toward sustainable energy solutions. A report from the Global Energy Monitor suggests that GIS technology will integrate effectively with renewable sources, such as solar and wind energy. This synergy could enhance grid stability and make power distribution more resilient. Concerns about long-term maintenance and operational costs remain prevalent, posing a challenge for energy providers.
Moreover, the technology's reliability is not without scrutiny. While GIS substations promise lower emissions, the environmental impact of manufacturing materials used in these systems draws attention. Continued innovation is needed to ensure that the lifecycle of GIS components adheres to sustainability goals. Balancing performance and ecological responsibility is crucial for the industry's future.